News & Insights
Insights
Insights
Insights
April 25, 2025
Donald Trump, a Powerful Supporter of the Euro
Insights
March 18, 2025
Oil in Troubled Waters
Insights
March 10, 2025
Trump 2.0 Reshaping the Mining Industry
1
2
3
Insights
March 10, 2025

President Donald Trump signed an Executive Order on February 25, 2025, instructing the Department of Commerce to investigate the national security implications of copper imports into the United States. The Executive Order requires an investigation into potential risks and vulnerabilities associated with foreign dependence of copper imports. The Department of Commerce was required to submit policy recommendations within 270 days. These recommendations may include measures such as tariff adjustments or incentives to stimulate domestic production.
The United States imports approximately 45% of the copper it consumes annually. Domestic production stands around 850,000 metric tons per year, with Arizona and Utah as key production hubs. The primary foreign suppliers of refined copper in the United States are Chile and Canada selling 800,000 tons in 2024.
The Executive Order highlights the strategic role of copper, stating that “copper’s derivative products play a vital role in defense applications, infrastructure, (…) and emerging technologies.” Furthermore, it shows the supply chain vulnerabilities in the country.
One of the critical concerns addressed in the Executive Order is the strong presence of Chinese companies in the global refining process. While China supplies only 2% of direct copper imports to the United States, it controls a significant share of global refining capacity. As mentioned in the Executive Order, “(…) over 50 percent of global smelting capacity and holding four of the top five largest refining facilities,” though it does not explicitly specify the Chinese competitors. The document raises concerns regarding the United States’ exposure to foreign refining infrastructure, particularly when controlled by a geopolitical and economic rival with substantial market leverage.
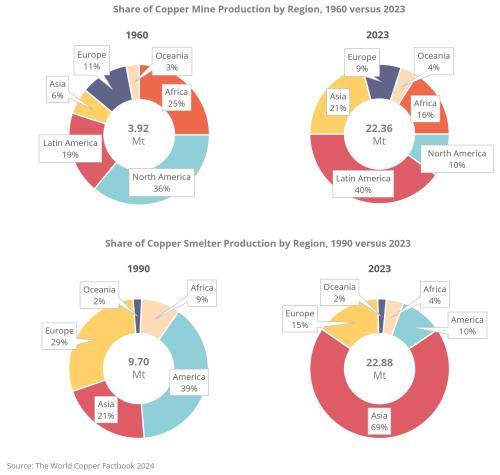
In response to these strategic vulnerabilities, there are indications that the Trump administration aims to bolster the domestic refining capacity and strengthen the U.S. mining industry. In the 1960s, North America had the highest copper mine production, while in the 1990s copper smelter production was significantly larger in the Americas than in other regions. However, this scenario has changed, as the charts below demonstrate. In the short term, such mining policy developments under the Trump administration may contribute to an increase in copper prices both in the United States and globally.
The price of copper per metric ton stands at $9,450.66 on the LME, whereas CME-listed copper priced at $10,254.10, representing an 8.5% price gap between London and Chicago. This arbitrage presents an opportunity for market traders to optimise their positions, particularly in anticipation of potential tariff adjustments which can occur in the next months.
In the long term, these changes drawn in the Executive Order could reinforce the U.S.-based copper producers. Companies such as Freeport-McMoRan (FCX), the largest U.S. copper producer, and Southern Copper Corporation (SCCO) are well-positioned to capitalise on increased domestic demand and policy-driven incentives.
COPPER PRODUCTION SHIFTED TO ASIA
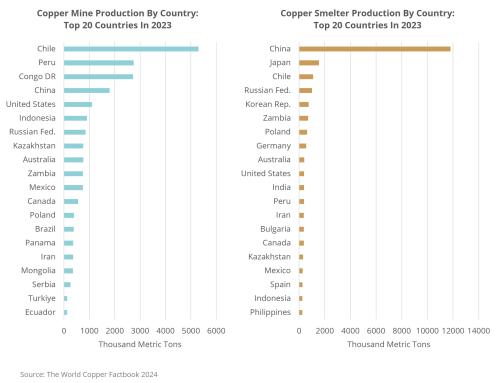
Chile dominates the global raw copper supply market, accounting for nearly a quarter of the world’s copper mine production, with an output of 5.3 million tons, while Peru remains the second-largest producer. However, the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) has made significant advances and is expected to surpass Peru by next year, becoming the world’s second-largest copper producer. This shift underscores the evolving dynamics of global copper supply, with emerging African economies—particularly the DRC—playing an increasingly influential role, largely due to Chinese investment in the region.
Simultaneously, the copper smelting industry has undergone a dramatic transformation. Between 1990 and 2023, Asia’s share of global copper smelter production surged from 21% to 69%, driven primarily by the rapid expansion of smelting capacity in China. This shift has significant economic implications, as China’s dominant position in copper smelting grants it considerable control over the processing of raw copper into refined copper, a critical stage in the supply chain. With Asia controlling such a large portion of global smelting capacity, the region is poised to continue influencing copper prices, solidifying its central role in the copper industry’s economics.
On the other hand, the Americas have experienced a sharp decline in their share of global copper smelting, dropping from 39% in 1990 to just 10% in 2023. Europe has also seen a decline, with its share falling from 29% to 15% over the same period (The World Copper Factbook 2024, p. 22) due to this situation, it seems the Trump administration is attempting to reverse it.
HISTORICAL PERFORMANCE
Between 2014 and 2020 the international copper price experienced significant volatility, which in turn impacted the stock market performance of companies like Freeport-McMoRan Inc (FCX)., whose shares also displayed considerable fluctuations during the same period. From 2021 ahead the copper price has increased which had a positive impact on FCX stock.
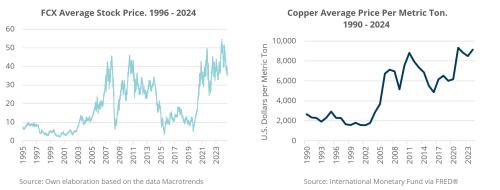
The Copper prices have seen substantial fluctuations over the past 15 years, shaped by global economic conditions, supply and demand factors, and geopolitical events. During the global financial crisis in 2008, copper prices dropped to about $1,300 per metric ton. The market recovered in the following years, reaching around $4,500 by 2011. After a decline, prices stabilised around $3,000 per metric ton in 2016. In 2021, copper prices surged past $4,500, driven primarily by high demand from the renewable energy sector and supply constraints because of the pandemic. As of February 2025, copper is trading at approximately $8,976 per metric ton globally, reflecting continued market volatility influenced by economic and political factors in the USA and high demand from the green industry.
INVESTMENT CASE
Copper is essential for various industries due to its unique properties. It plays a key role in traditional industries, such as electrical wiring, motors, and generators. Additionally, copper is also critical in the green industry, especially in renewable energy technologies and electric vehicles, where its excellent conductivity and durability are indispensable. Playing an important role in both the traditional industry and the emerging green industry, copper prices are expected to increase in the next few years because of this situation.
Freeport-McMoRan Inc. (FCX) could be an attractive opportunity due to its significant role in the copper market in the United States. As one of the largest traded copper producers, FCX stands to benefit from the high demand for copper in the market and the policies outlined in Donald Trump's Executive Order. With strong support expected from the Trump Administration to traditional infrastructure projects and the Stargate project in the coming years, copper prices are expected to rise in both the USA and globally due to it being an essential element in these infrastructure projects.
Furthermore, as copper prices have surged in recent years, FCX's stocks has experienced positive performance. The future tariff expected to be imposed by Donald Trump on the import of copper could develop a significant impact on the consumer in the USA. However, a drop in price is not expected if demand in the industry remains high. Consequently, this could create a positive scenario for copper producers in the United States.
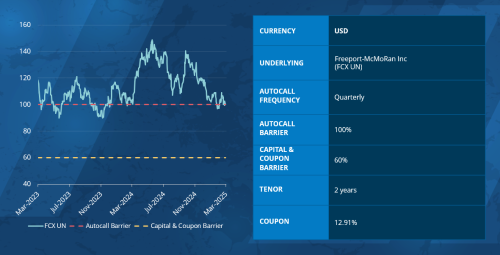
Phoenix Memory Autocall | Product Snapshot
For informational purposes only. Not investment advice.
Insights
March 10, 2025
Trump 2.0 Reshaping the Mining Industry

President Donald Trump signed an Executive Order on February 25, 2025, instructing the Department of Commerce to investigate the national security implications of copper imports into the United States. The Executive Order requires an investigation into potential risks and vulnerabilities associated with foreign dependence of copper imports. The Department of Commerce was required to submit policy recommendations within 270 days. These recommendations may include measures such as tariff adjustments or incentives to stimulate domestic production.
The United States imports approximately 45% of the copper it consumes annually. Domestic production stands around 850,000 metric tons per year, with Arizona and Utah as key production hubs. The primary foreign suppliers of refined copper in the United States are Chile and Canada selling 800,000 tons in 2024.
The Executive Order highlights the strategic role of copper, stating that “copper’s derivative products play a vital role in defense applications, infrastructure, (…) and emerging technologies.” Furthermore, it shows the supply chain vulnerabilities in the country.
One of the critical concerns addressed in the Executive Order is the strong presence of Chinese companies in the global refining process. While China supplies only 2% of direct copper imports to the United States, it controls a significant share of global refining capacity. As mentioned in the Executive Order, “(…) over 50 percent of global smelting capacity and holding four of the top five largest refining facilities,” though it does not explicitly specify the Chinese competitors. The document raises concerns regarding the United States’ exposure to foreign refining infrastructure, particularly when controlled by a geopolitical and economic rival with substantial market leverage.
In response to these strategic vulnerabilities, there are indications that the Trump administration aims to bolster the domestic refining capacity and strengthen the U.S. mining industry. In the 1960s, North America had the highest copper mine production, while in the 1990s copper smelter production was significantly larger in the Americas than in other regions. However, this scenario has changed, as the charts below demonstrate. In the short term, such mining policy developments under the Trump administration may contribute to an increase in copper prices both in the United States and globally.
The price of copper per metric ton stands at $9,450.66 on the LME, whereas CME-listed copper priced at $10,254.10, representing an 8.5% price gap between London and Chicago. This arbitrage presents an opportunity for market traders to optimise their positions, particularly in anticipation of potential tariff adjustments which can occur in the next months.
In the long term, these changes drawn in the Executive Order could reinforce the U.S.-based copper producers. Companies such as Freeport-McMoRan (FCX), the largest U.S. copper producer, and Southern Copper Corporation (SCCO) are well-positioned to capitalise on increased domestic demand and policy-driven incentives.

COPPER PRODUCTION SHIFTED TO ASIA
Chile dominates the global raw copper supply market, accounting for nearly a quarter of the world’s copper mine production, with an output of 5.3 million tons, while Peru remains the second-largest producer. However, the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) has made significant advances and is expected to surpass Peru by next year, becoming the world’s second-largest copper producer. This shift underscores the evolving dynamics of global copper supply, with emerging African economies—particularly the DRC—playing an increasingly influential role, largely due to Chinese investment in the region.
Simultaneously, the copper smelting industry has undergone a dramatic transformation. Between 1990 and 2023, Asia’s share of global copper smelter production surged from 21% to 69%, driven primarily by the rapid expansion of smelting capacity in China. This shift has significant economic implications, as China’s dominant position in copper smelting grants it considerable control over the processing of raw copper into refined copper, a critical stage in the supply chain. With Asia controlling such a large portion of global smelting capacity, the region is poised to continue influencing copper prices, solidifying its central role in the copper industry’s economics.
On the other hand, the Americas have experienced a sharp decline in their share of global copper smelting, dropping from 39% in 1990 to just 10% in 2023. Europe has also seen a decline, with its share falling from 29% to 15% over the same period (The World Copper Factbook 2024, p. 22) due to this situation, it seems the Trump administration is attempting to reverse it.

HISTORICAL PERFORMANCE
Between 2014 and 2020 the international copper price experienced significant volatility, which in turn impacted the stock market performance of companies like Freeport-McMoRan Inc (FCX)., whose shares also displayed considerable fluctuations during the same period. From 2021 ahead the copper price has increased which had a positive impact on FCX stock.

The Copper prices have seen substantial fluctuations over the past 15 years, shaped by global economic conditions, supply and demand factors, and geopolitical events. During the global financial crisis in 2008, copper prices dropped to about $1,300 per metric ton. The market recovered in the following years, reaching around $4,500 by 2011. After a decline, prices stabilised around $3,000 per metric ton in 2016. In 2021, copper prices surged past $4,500, driven primarily by high demand from the renewable energy sector and supply constraints because of the pandemic. As of February 2025, copper is trading at approximately $8,976 per metric ton globally, reflecting continued market volatility influenced by economic and political factors in the USA and high demand from the green industry.
INVESTMENT CASE
Copper is essential for various industries due to its unique properties. It plays a key role in traditional industries, such as electrical wiring, motors, and generators. Additionally, copper is also critical in the green industry, especially in renewable energy technologies and electric vehicles, where its excellent conductivity and durability are indispensable. Playing an important role in both the traditional industry and the emerging green industry, copper prices are expected to increase in the next few years because of this situation.
Freeport-McMoRan Inc. (FCX) could be an attractive opportunity due to its significant role in the copper market in the United States. As one of the largest traded copper producers, FCX stands to benefit from the high demand for copper in the market and the policies outlined in Donald Trump's Executive Order. With strong support expected from the Trump Administration to traditional infrastructure projects and the Stargate project in the coming years, copper prices are expected to rise in both the USA and globally due to it being an essential element in these infrastructure projects.
Furthermore, as copper prices have surged in recent years, FCX's stocks has experienced positive performance. The future tariff expected to be imposed by Donald Trump on the import of copper could develop a significant impact on the consumer in the USA. However, a drop in price is not expected if demand in the industry remains high. Consequently, this could create a positive scenario for copper producers in the United States.
Phoenix Memory Autocall | Product Snapshot
For informational purposes only. Not investment advice.

